Spring Security 授权
1.简介
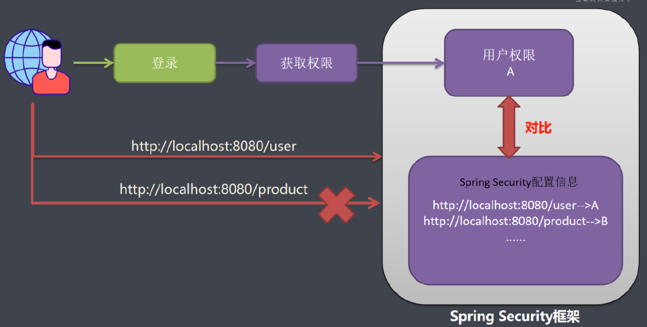
在我们应用系统里面,如果想要控制用户权限,需要有2部分数据
- 系统配置信息数据:写着系统里面有哪些URL,每一个url拥有哪些权限才允许被访问。
- 另一份数据就是用户权限信息:请求用户拥有权限系统用户发送一个请求:系统配置信息和用户权限信息作比对,如果比对成功则允许访问。
2.Spring Security授权
2.1 内置表达式
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
hasRole(String role) | Returns true if the current principal has the specified role.For example, hasRole('admin')By default if the supplied role does not start with ‘ROLE_’ it will be added. This can be customized by modifying the defaultRolePrefix on DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler. |
hasAnyRole(String… roles) | Returns true if the current principal has any of the supplied roles (given as a comma-separated list of strings).For example, hasAnyRole('admin', 'user')By default if the supplied role does not start with ‘ROLE_’ it will be added. This can be customized by modifying the defaultRolePrefix on DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler. |
hasAuthority(String authority) | Returns true if the current principal has the specified authority.For example, hasAuthority('read') |
hasAnyAuthority(String… authorities) | Returns true if the current principal has any of the supplied authorities (given as a comma-separated list of strings)For example, hasAnyAuthority('read', 'write') |
principal | Allows direct access to the principal object representing the current user |
authentication | Allows direct access to the current Authentication object obtained from the SecurityContext |
permitAll | Always evaluates to true |
denyAll | Always evaluates to false |
isAnonymous() | Returns true if the current principal is an anonymous user |
isRememberMe() | Returns true if the current principal is a remember-me user |
isAuthenticated() | Returns true if the user is not anonymous |
isFullyAuthenticated() | Returns true if the user is not an anonymous or a remember-me user |
hasPermission(Object target, Object permission) | Returns true if the user has access to the provided target for the given permission. For example, hasPermission(domainObject, 'read') |
hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission) | Returns true if the user has access to the provided target for the given permission. For example, hasPermission(1, 'com.example.domain.Message', 'read') |
2.2 url安全表达式
基于web访问使用表达式保护url请求路径
设置url访问权限
// 设置/user开头的请求需要ADMIN权限 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("ADMIN"); // 设置/product 开头的请求需要ADMIN 或者 PRODUCT权限 并且访问的IP是127.0.0.1 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/product/**").access( "hasAnyRole('ADMIN','PRODUCT') and hasIpAddress('127.0.0.1')" );MyAccessDeniedHandler自定义权限不足类
@Component public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler { @Override public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); response.getWriter().write("权限不足,请联系管理员."); } }设置用户对应的角色权限
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>(); if ("admin".equalsIgnoreCase(user.getUsername())) { authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN")); } else { authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_PRODUCT")); }
2.3 在web安全表达式中引用 自定义的Bean授权
/**
* 自定义bean授权
*/
@Component
public class MyAuthorizationService {
/**
* 检查用户是否有权限
*
* @param authentication 认证信息
* @param request 请求对象
* @return
*/
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request) {
UserDetails principal = (UserDetails) authentication.getPrincipal();
String username = principal.getUsername();
// 获取用户权限的集合
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = (Collection<GrantedAuthority>)
principal.getAuthorities();
// 如果用户名为admin 直接返回true
if ("admin".equalsIgnoreCase(username)) {
return true;
} else {
// 获取请求路径
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
if (requestURI.contains("/user")) {
// 循环判断用户的权限集合是否包含ROLE_ADMIN
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
if ("ROLE_ADMIN".equals(authority.getAuthority())) {
return true;
}
}
}
if (requestURI.contains("/product")) {
// 循环判断用户的权限集合是否包含ROLE_PRODUCT
for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {
if ("ROLE_PRODUCT".equals(authority.getAuthority())) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 检查ID是否大于10
*
* @param authentication 认证信息
* @param request 请求对象
* @return
*/
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request, Integer id) {
if (id > 10) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/{id}")
.access("@myAuthorizationService.check(authentication,request,#id)");
2.4 method安全表达式
/**
* Security配置类
*/
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)//开启注解支持
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
针对方法级别的访问控制比较复杂, spring security 提供了4种注解分别是
@PreAuthorize
进入方法前的权限验证
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")//需要ADMIN权限@PostAuthorize
在方法执行后再进行权限验证,适合验证带有返回值的权限, Spring EL 提供返回对象能够在表达式语言中获取到返回对象的 returnObject
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.username==authentication.principal.username")//returnObject返回参数 只能自己查询自己的信息@PreFilter
用来对集合类型的参数进行过滤, 将不符合条件的元素剔除集合
用来对集合类型的参数进行过滤, 将不符合条件的元素剔除集合@PostFilter
用来对集合类型的返回值进行过滤, 将不符合条件的元素剔除集合
@PostFilter("filterObject.id%2!=0")//剔除所有基数的用户信息
3.基于数据库的RBAC数据模型的权限控制
我们开发一个系统,必然面临权限控制的问题,不同的用户具有不同的访问、操作、数据权限。形成理论的权限控制模型有:自主访问控制(DAC: Discretionary Access Control)、强制访问控制MAC: Mandatory Access Control)、基于属性的权限验证(ABAC: Attribute-Based AccessControl)等。最常被开发者使用也是相对易用、通用的就是RBAC权限模型(Role-Based AccessControl)
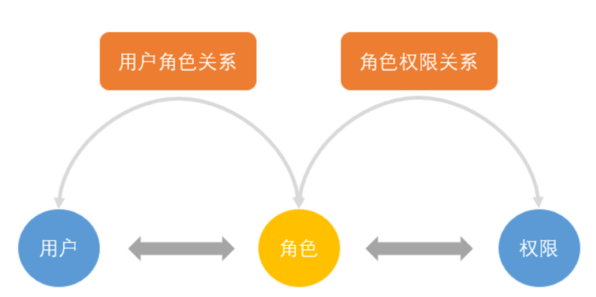
3.1 RBAC简介
RBAC权限模型(Role-Based Access Control)即:基于角色的权限控制。模型中有几个关键的术语:
- 用户:系统接口及访问的操作者
- 权限:能够访问某接口或者做某操作的授权资格
- 角色:具有一类相同操作权限的总称
RBAC权限模型核心授权逻辑如下:
- 某用户是什么角色?
- 某角色具有什么权限?
- 通过角色对应的权限推导出用户的权限
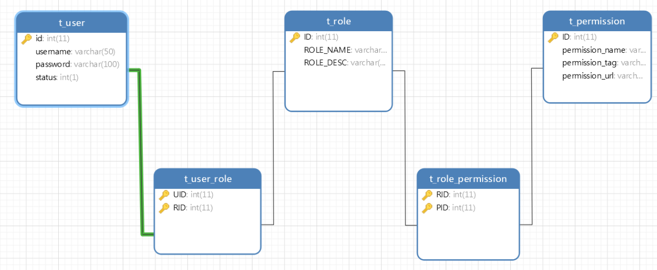
3.2 基于RBAC设计权限表结构
- 一个用户有一个或多个角色
- 一个角色包含多个用户
- 一个角色有多种权限
- 一个权限属于多个角色
3.3 基于Spring Security 实现RBAC权限管理
给登录用户授权
//MyUserDetailsService类 // 基于数据库查询用户对应的权限 List<Permission> permissionList = permissionService.findByUserId(user.getId()); for (Permission permission:permissionList) { authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(permission.getPermissionTag())); }设置访问权限
//SecurityConfig类 // 查询数据库所有权限列表 List<Permission> list = permissionService.list(); for (Permission permission : list) { // 添加请求权限 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers(permission.getPermissionUrl()) .hasAuthority(permission.getPermissionTag()); }
4.基于页面端标签的权限控制
<!--添加thymeleaf为SpringSecurity提供的标签 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security">
常用标签:
判断用户是否已经登陆认证,引号内的参数必须是isAuthenticated()。
sec:authorize=“isAuthenticated()”
获得当前用户的用户名,引号内的参数必须是name。
sec:authentication=“name”
判断当前用户是否拥有指定的权限。引号内的参数为权限的名称。
sec:authorize=“hasRole(‘role’)”